Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D) is a powerful analytical tool that enables the measurement of both mass changes and viscoelastic properties of thin films at the nanoscale, in a liquid environment, thereby providing critical insights into various biological and chemical processes. This blog delves into the key applications of QCM-D in the pharmaceutical industry, highlighting its importance in drug development, formulation, and quality control.

What is QCM-D?
At the core of the QCM-D technology is a quartz crystal that is oscillated at its resonant frequency. The resonant frequency is dependent on the mass of the crystal and any change to the mass is reflected in a change in frequency. When a mass is deposited onto the sensor surface, the frequency decreases proportionally to the mass and vice versa (Figure 1). QCM-D can detect mass changes in the nanogram range. The energy dissipation of the quartz crystal provides information about the viscoelastic properties of the material bound to the crystal.
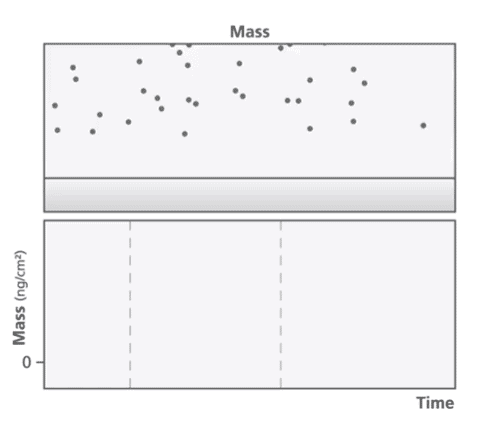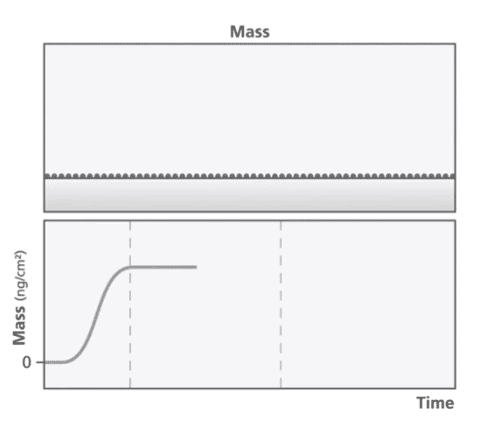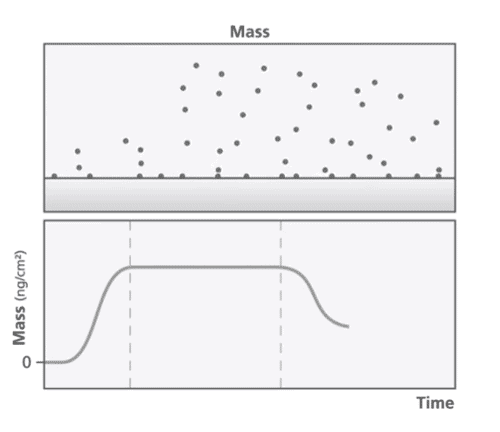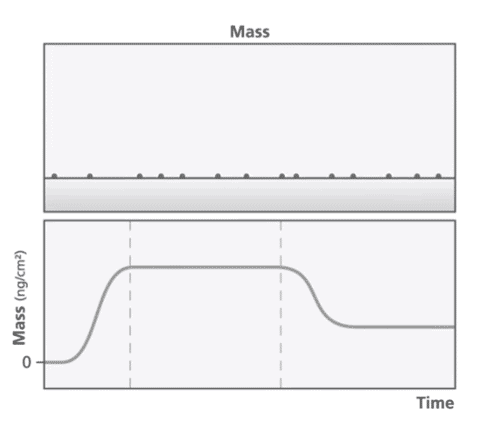
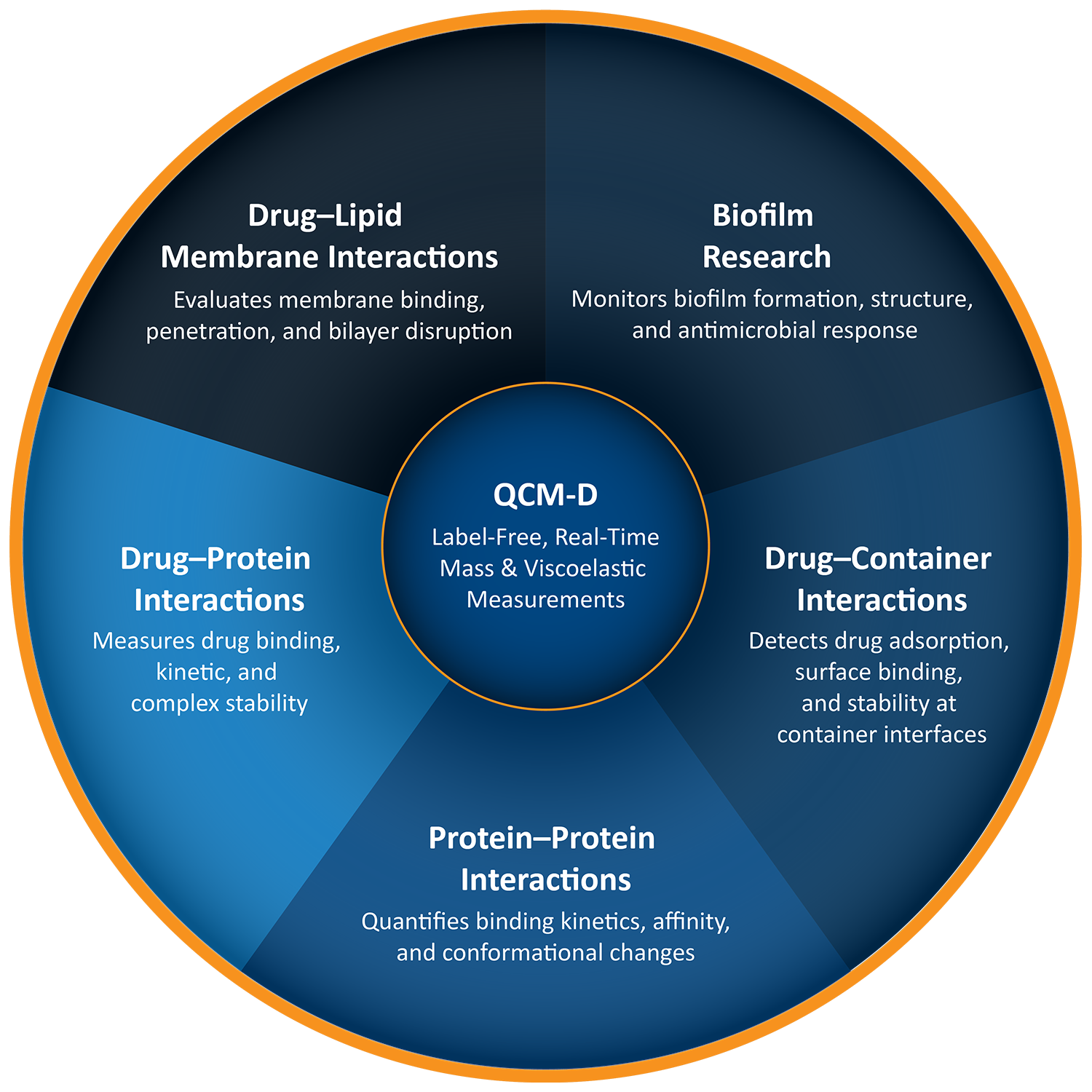
QCM-D Applications in Pharmaceutical Sciences
The real-time monitoring capability of QCM-D enables the observation of dynamic processes as they occur which is particularly useful for studying the kinetics of drug interactions and the formation or disruption of biofilms. In addition, QCM-D is a non-destructive technique meaning that the samples can be further analyzed using other methods if needed. This is advantageous in pharmaceutical research, where sample preservation is often important.
QCM-D has several key applications in pharma industry including:
Investigating Drug – Container Interaction
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) can be applied to investigate how drug molecules interact with pharmaceutical container surfaces, such as vials, syringes, or infusion bags.1 By measuring changes in mass and viscoelastic properties at the container interface, QCM-D provides insights into adsorption, surface binding, or aggregation phenomena. Key applications include:
Surface Adsorption Monitoring:
QCM-D can detect if a drug binds to or deposits on container surfaces, which can reduce effective drug concentration.
Real-time Kinetics:
Association and dissociation rates of drug adsorption can be observed, helping predict stability and shelf-life.
Viscoelastic Characterization:
Dissipation measurements reveal whether adsorbed layers are rigid or soft, indicating potential aggregation or structural changes.
Formulation Optimization:
QCM-D helps assess how buffer composition, pH, or excipients influence drug–surface interactions, enabling formulation strategies that minimize undesirable adsorption.
Studying Protein – Protein Interactions
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) play a foundational role in biologics development, stability assessment, and formulation optimization. QCM-D enables detailed characterization of these interactions by simultaneously tracking mass increase and viscoelastic changes, supporting kinetic analysis, conformational evaluation, competitive binding studies, and stability profiling.2 Several features make QCM-D particularly effective for PPI analysis in pharmaceutical research:
Label-free Measurement:
Interactions can be monitored without chemical tagging, preserving native binding behavior and ensuring that affinity measurements reflect true molecular recognition.
Real-time Kinetic Monitoring:
Continuous tracking of frequency and dissipation provides direct association and dissociation rates. This makes QCM-D well suited for evaluating antibody–antigen affinities, Fc receptor interactions, and competitive binding scenarios where ligands, inhibitors, or competing proteins are introduced sequentially.
Sensitivity to Structural & Viscoelastic Changes:
QCM-D detects conformational shifts, soft layer formation, and multilayer buildup. The dissipation signal reveals structural rearrangements, partial unfolding, clustering, and hydration changes which are critical for identifying aggregation-prone interactions, evaluating excipient effects, and assessing layer organization during formulation development.
Performance in Physiologically Relevant Environments:
QCM-D operates effectively in complex buffers, excipient-rich matrices, or biologically relevant media. This enables realistic assessments of interaction stability under varying pH, ionic strength, and formulation conditions, providing insight into how protein complexes behave outside of idealized laboratory settings.
Studying Drug-Protein Interactions
QCM-D can be used to study drug–protein interactions by measuring how small-molecule or biologic drugs bind to immobilized target proteins on the sensor surface.3 As the drug interacts with the protein layer, changes in resonance frequency indicate mass changes, while changes in dissipation reveal alterations in the viscoelastic properties of the bound layer. These signals allow researchers to quantify binding kinetics (ka, kd), affinity (KD), and the stability of the drug–protein complex. QCM-D can also detect conformational changes, competitive binding events, and the influence of formulation conditions such as pH, ionic strength, or excipients. This makes it a powerful tool for characterizing mechanism of action, screening drug candidates, and optimizing formulation behavior under physiologically relevant conditions.
Studying Drug- Lipid Membrane Interactions
QCM-D can be used to study drug–lipid interactions by monitoring how a drug molecule binds to or disrupts a supported lipid layer formed on the sensor surface.4 As the drug associates with the lipid membrane, QCM-D detects frequency shifts that indicate mass uptake or loss and dissipation changes that reflect alterations in membrane structure, fluidity, or integrity. These measurements provide insight into binding affinity, insertion depth, membrane penetration, bilayer destabilization, and the effects of formulation variables such as pH, surfactants, or excipients. This makes QCM-D a valuable tool for characterizing drug–membrane mechanisms, evaluating permeability and adsorption behavior, and optimizing lipid-based drug delivery systems.
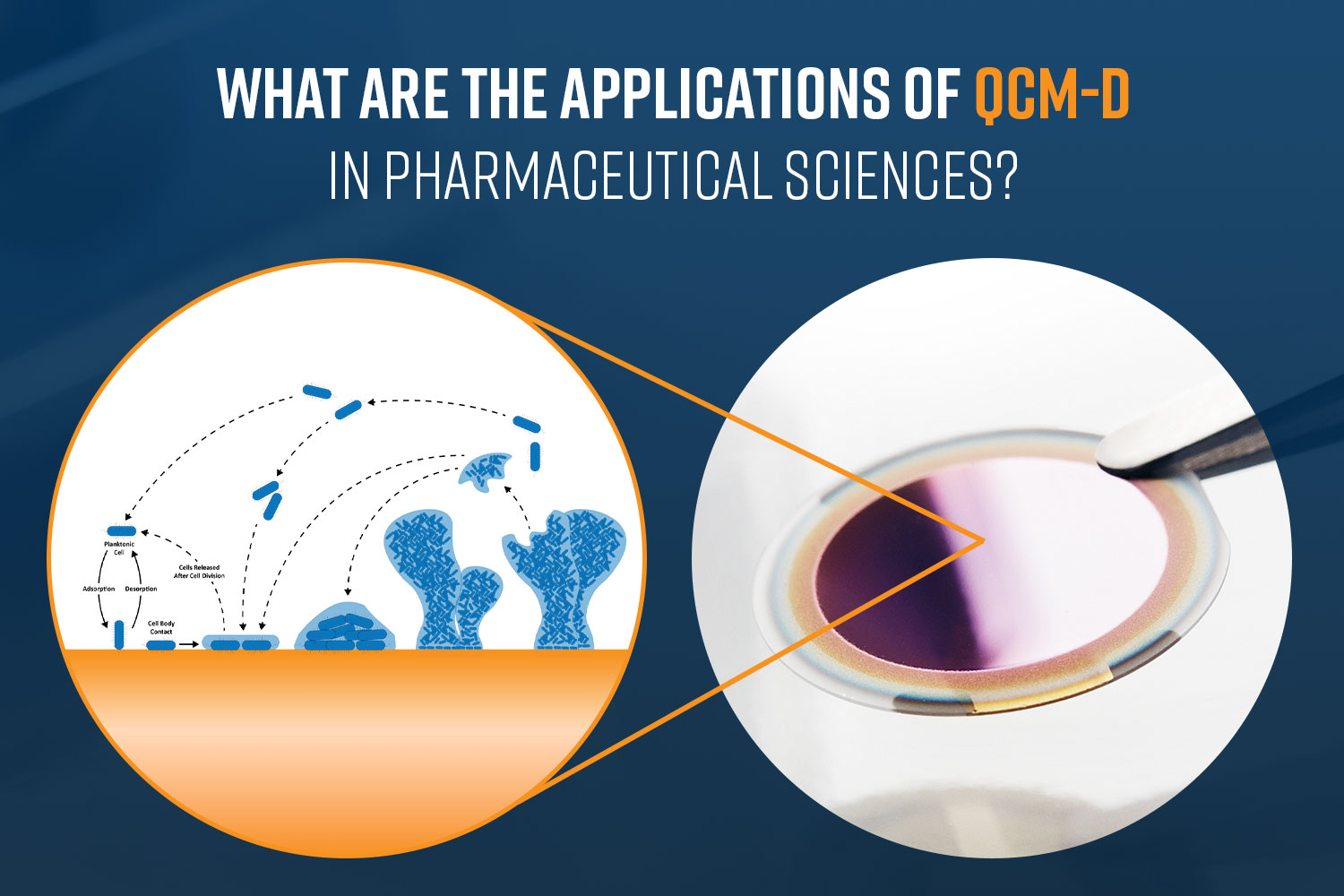
Biofilm Research
Biofilms are communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and are encased in a protective matrix (shown in Figure 3). They are a significant concern in pharmaceutical and medical settings due to their resistance to antibiotics. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) is a powerful tool for investigating biofilm formation and behavior, which is critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing, drug delivery systems, and contamination control.5 QCM-D monitors both mass changes and viscoelastic properties of biofilms in real time, providing detailed mechanistic insights. Key applications include:
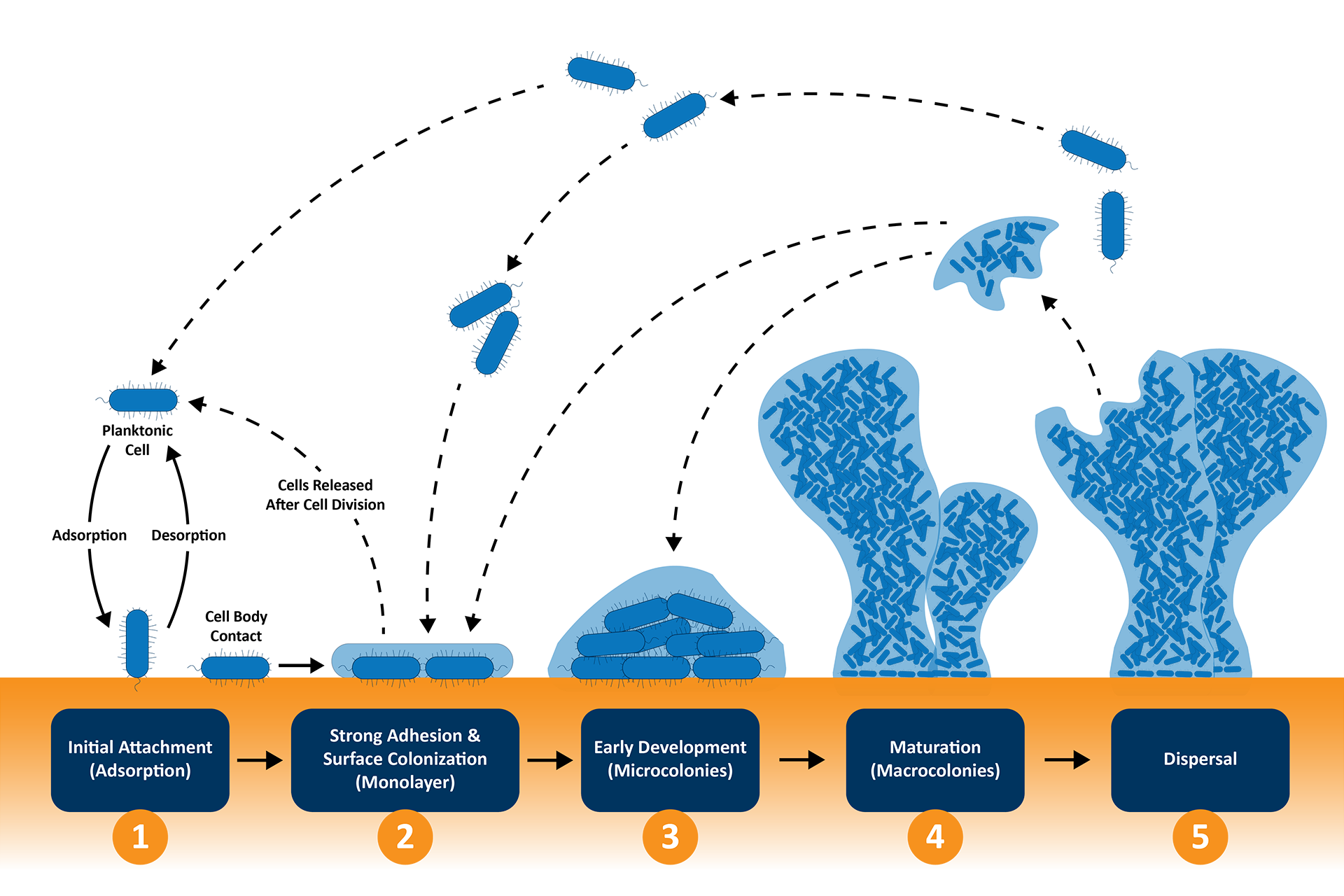
Biofilm Formation Monitoring:
QCM-D can track initial microbial adhesion and subsequent biofilm growth on surfaces such as medical devices, packaging materials, or bioreactor components.
Real-time Kinetics:
Association and detachment events can be measured, helping understand biofilm dynamics under different environmental conditions.
Structural Characterization:
Changes in dissipation reveal the viscoelastic properties of biofilms, including density, hydration, and extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) composition.
Antimicrobial Efficacy Testing:
QCM-D allows evaluation of how drugs, coatings, or disinfectants affect biofilm adhesion, growth, and mechanical stability.
Design of Surfaces:
Insights from QCM-D guide the design of surfaces and formulations that reduce biofilm formation, improving sterility and product safety.
Conclusion:
QCM-D is a versatile and powerful tool that has found numerous applications in the pharmaceutical industry. From studying drug-protein interactions to ensuring the stability of formulations, QCM-D provides critical insights that drive innovation and improve the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. As the field of pharmaceuticals continues to evolve, the role of QCM-D is likely to grow, offering even more opportunities for its application in drug development and quality control.
References:
- Weidman, J.; Mathews, L.; Gokhale, K. Quartz Crystal Microbalance as a predictive tool for Drug-Material of Construction interactions in intravenous protein drug administration. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, 112 (12), 3154–3163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2023.07.019. ↩︎
- Migoń, D.; Wasilewski, T.; Suchy, D. Application of QCM in Peptide and Protein-Based Drug product development. Molecules 2020, 25 (17), 3950. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173950. ↩︎
- Al-Husseini, J. K.; Stanton, N. J.; Selassie, C. R. D.; Johal, M. S. The binding of drug molecules to serum albumin: The effect of drug hydrophobicity on binding strength and protein desolvation. Langmuir 2019, 35 (52), 17054–17060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b02318. ↩︎
- Birchenough, H. L.; Jowitt, T. A. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D): Preparing Functionalized Lipid Layers for the Study of Complex Protein–Ligand Interactions. Methods in Molecular Biology 2021, 2263, 183–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1197-5_7. ↩︎
- Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Malakar, P. K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. New Insights into the Mediation of Biofilm Formation by Three Core Extracellular Polysaccharide Biosynthesis Pathways in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2025, 26 (8), 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083780. ↩︎